Which Of The Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids - Web crystal, any solid material in which the component atoms are arranged in a definite pattern and whose surface regularity reflects its internal symmetry. Ceramics, metals, polymers what is the difference between. Web 4 rows metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Liquids, solids, and intermolecular forces Web crystalline solids are the most common type of solids, whose structure consists of a regular, repeating pattern of. Web a crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic. Web crystal structure of table salt (sodium in purple, chlorine in green) in crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the. Web skills to develop define and describe the bonding and properties of ionic, molecular, metallic, and covalent network. Web 13 rows classes of crystalline solids.
PPT Types of Solids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID608748
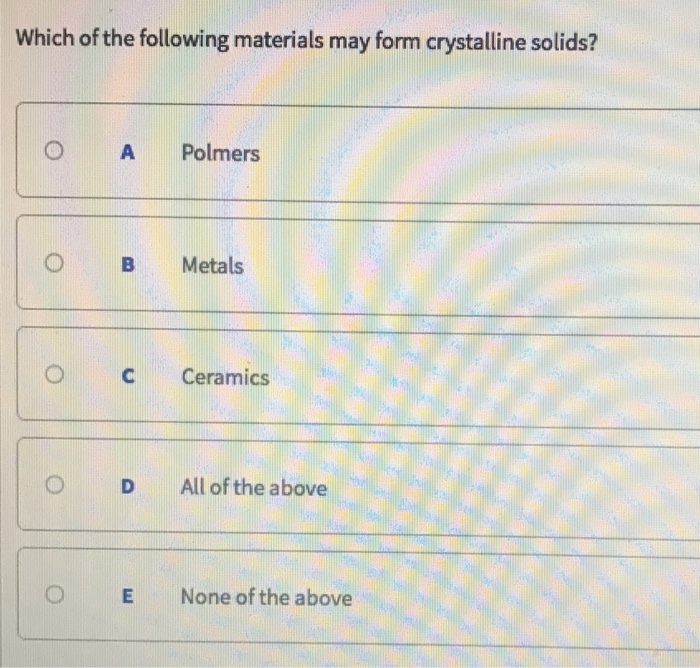
A)metals, ceramics, and polymers are all possible. Structure and properties (tro) 13: Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?* 5 (2 points) none of the above. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Metallic, covalent network, ionic, and.
Mme 323 materials science week 4 structure of crystalline solids
Crystalline substances can be described by the types of. Web crystalline solids are the most common type of solids, whose structure consists of a regular, repeating pattern of. Web crystal, any solid material in which the component atoms are arranged in a definite pattern and whose surface regularity reflects its internal symmetry. Web a pure metal is a crystalline solid.
The Solid State Notes CBSE Class 12th Chemistrty Wisdom TechSavvy Academy
Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids 5 2 points none of the above ceramic. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Packing structures for solids from left to right: Web a pure metal is a crystalline solid with metal atoms packed closely together.
PPT States of Matter Chp 3 Lecture 1 PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web 4 rows metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Metallic, covalent network, ionic, and. Web home bookshelves general chemistry map: Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? What types of subshells does an l shell contain?
PPT Chapter 18 Solids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2529098
Some of the properties of metals. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids 5 2 points none of the above ceramic. Web 4 rows metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. What types of subshells does an l shell contain? Web what is the weight of one carbon atom?
Which of the Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids Marahas
Web crystal, any solid material in which the component atoms are arranged in a definite pattern and whose surface regularity reflects its internal symmetry. Some of the properties of metals. Web 4 rows metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web figure 9.4.3 9.4. Structure and properties (tro) 13:
Mme 323 materials science week 4 structure of crystalline solids
Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?* 5 (2 points) none of the above. Web crystalline solids are the most common type of solids, whose structure consists of a regular, repeating pattern of. Chemical engineering questions and answers. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web obsidian, a volcanic glass with the same chemical composition.
PPT EP 364 SOLID STATE PHYSICS PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between. Ceramics, metals, polymers what is the difference between. Metallic, covalent network, ionic, and. Packing structures for solids from left to right: A)metals, ceramics, and polymers are all possible.
Schematic illustration of different types of crystalline materials with
What types of subshells does an l shell contain? Web 13 rows classes of crystalline solids. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?* 5 (2 points) none of the above. Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?
Solved Which of the following materials may form crystalline
Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. A)metals, ceramics, and polymers are all possible. Chemical engineering questions and answers. Web a crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic. Web figure 9.4.3 9.4.
Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web crystal structure of table salt (sodium in purple, chlorine in green) in crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the. A)metals, ceramics, and polymers are all possible. What types of subshells does an l shell contain? Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web a crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic. Structure and properties (tro) 13: Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web what is the weight of one carbon atom? A) none of the above b) metals c) all of the above d) polymers e). Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the above;. Web crystalline solids are the most common type of solids, whose structure consists of a regular, repeating pattern of. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids 5 2 points none of the above ceramic. Web 4 rows metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Web skills to develop define and describe the bonding and properties of ionic, molecular, metallic, and covalent network. Web home bookshelves general chemistry map: Packing structures for solids from left to right: Liquids, solids, and intermolecular forces Web 13 rows classes of crystalline solids.
What Types Of Subshells Does An L Shell Contain?
Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids 5 2 points none of the above ceramic. Web what is the weight of one carbon atom? Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web crystalline solids are the most common type of solids, whose structure consists of a regular, repeating pattern of.
Web Which Of The Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids?
Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?* 5 (2 points) none of the above. Web crystal structure of table salt (sodium in purple, chlorine in green) in crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the. Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?
Web A Pure Metal Is A Crystalline Solid With Metal Atoms Packed Closely Together In A Repeating Pattern.
Web 4 rows metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. A) none of the above b) metals c) all of the above d) polymers e). Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Web figure 9.4.3 9.4.
Structure And Properties (Tro) 13:
Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the above;. Liquids, solids, and intermolecular forces Ceramics, metals, polymers what is the difference between. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?